Ethernet Market
As data centers push for greater data transmission efficiency and novel connectivity solutions, the ethernet market is set to experience a compound annual growth rate of 5.2% between 2024 and 2031. This rise driven by the growth of emerging applications amongst next generation data centers, IoT devices and the shift towards 5G networks will continue to push technological advancements in performance capability and scalability as the next generation of data centers emerge.
The ethernet market is categorized into four segments, each with their own applications and growth trajectories. The four segments include 25G, 50G, 100G, and other categories.
25G:
. Cost optimization
. Targeting enterprise networks and data centers
. Driven by the increased demand for cloud services.
50G:
. Applications requiring higher bandwidth without the cost associated with 100G
. Driven by the rising demand for streaming and IoT applications
100G:
. High capacity
. High performance
. Ideal applications for expanding operations and telecom
. Driven by the emerging growth of 5G networks and big data analytics
Other categories and high-growth segments:
. 400G and beyond
. Driven by technological development in telecommunications and growing demand for higher bandwidth applications in AI and machine learning
Currently the market is defined by multiple key drivers and challenges steering technological advancements augmenting data analytics and automating processes amongst applications such as AI and machine learning. The emerging growth of 5G networks has also pushed the boundaries of connectivity, empowering advancements in IoT devices and smart applications.
Key applications


Scaling cloud services, especially in edge computing, requires networks that can handle high data throughput efficiently
Cloud data centers


Telecom networks
Telecom infrastructure will increasingly rely on 800GbE for high-speed connectivity, especially as 5G networks deploy


AI/ML
800GbE supports faster processing of large datasets for AI model training and inference, essential in research and business applications
The 800GbE and 1.6TbE market outlook
As data centers continue to evolve and the demand for faster, more efficient network infrastructure grows, the Ethernet market is progressing toward ever-higher speeds, with 800GbE and 1.6TbE technologies playing key roles. The need for higher bandwidth to support next-generation applications such as 5G, AI/ML, cloud computing, and IoT is pushing Ethernet technology to its limits. The 800GbE market alone is expected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 7.5% between 2024 and 2030 as the demand for high-speed, high-capacity connections grow across large-scale data centers and telecom networks.
Beyond 800GbE, the 1.6TbE market is gaining attention, representing the next leap in Ethernet technology for the most demanding applications in high-performance computing, telecom backbones, and data-intensive workloads. 1.6TbE solutions, with their ability to support 1.6 Terabits per second of throughput, will drive innovation in network scalability, enabling data centers to handle petabytes of data across global infrastructures.
Key drivers of the 800GbE and 1.6TbE markets
-
Rising data demand: The continuous explosion in data generated by cloud services, 5G, AI, machine learning, and big data analytics is pushing the demand for higher network speeds.
-
5G and beyond: The global rollout of 5G networks and future plans for 6G create significant bandwidth demands, making the adoption of 800GbE and 1.6TbE essential for telecom networks.
-
AI/ML and high-performance computing (HPC): AI/ML models, especially in real-time data processing and training, require massive bandwidth, further driving the need for higher Ethernet speeds.
-
Data center and telecom network evolution: Hyper-scale data centers along with telecom backbones require faster and more efficient solutions to scale with increasing user demand and data traffic.
800GbE market segmentation
The 800GbE market is anticipated to grow in various segments, including: 25G, 50G, 100G, 200G, and 400G transition to 800GbE.
-
As 400GbE adoption becomes more widespread, 800GbE will provide a vital step forward, supporting applications with higher capacity, including cloud, telecom, and large-scale enterprise networks.
Key applications of 800GbE


Cloud data centers
Scaling cloud services, especially in edge computing, requires networks that can handle high data throughput efficiently


Telecom networks
Telecom infrastructure will increasingly rely on 800GbE for high-speed connectivity, especially as 5G networks deploy


AI/ML
800GbE supports faster processing of large datasets for AI model training and inference, essential in research and business applications
1.6TbE market and outlook
The 1.6TbE standard, while still in its early stages, is expected to see significant deployment in the 2027-2032 window. This higher-speed technology will support the largest-scale data centers, telecom backbones, and emerging applications such as AI-driven network optimization and cloud-scale data processing. 1.6TbE is expected to follow 800GbE, leveraging breakthroughs in optical interconnects, SerDes technology, and advanced modulation techniques to enable ultra-high-speed, low-latency connections.
-
1.6TbE will be primarily driven by the demand for massive data throughput in cloud data centers, 5G/6G, and telecom infrastructures.
-
It will likely feature advanced optical transceivers to handle the enormous bandwidth requirements and the transition from 800GbE will offer a cost-effective step for large-scale operators.
SerDes line rates and their impact on the 800GbE and 1.6TbE markets
The serial deserializer (SerDes) technology plays a pivotal role in enabling the high-speed transmission required for both 800GbE and 1.6TbE Ethernet technologies. SerDes operates by converting parallel data streams into serial data for high-speed transmission, and then converting it back for processing at the receiver end. Advances in SerDes technology will allow Ethernet speeds to scale beyond the current 400GbE limits, enabling 800GbE and 1.6TbE to become a reality.
SerDes line rates
-
SerDes for 800GbE: The typical line rate for 800GbE is 112 Gbps per lane, which uses PAM-4 (pulse amplitude modulation) for data transmission. The 400GbE standard uses 56 Gbps per lane, and 800GbE effectively doubles this, requiring optical interconnects capable of supporting higher speeds.
-
SerDes for 1.6TbE: The line rate for 1.6TbE is 224 Gbps per lane, also using PAM-4 modulation. This provides a significant boost in speed, enabling ultra-fast transmission for high-demand applications like large-scale cloud infrastructures, 5G backhaul, and high-performance computing (HPC).
Key drivers for growth
-
5G and beyond: The global deployment of 5G and future 6G networks will significantly push the need for higher-speed Ethernet solutions to meet the demands for ultra-low-latency and massive bandwidth.
-
Cloud computing: Cloud and hyperscale data centers are some of the largest consumers of bandwidth and will be key adopters of 800GbE and 1.6TbE technologies.
-
Telecom network upgrades: Telecom providers will be at the forefront of 1.6TbE adoption, as they need the next level of performance to support 5G backhaul and large-scale infrastructure.
-
Cost reduction in optical transceivers: As the cost of optical transceivers (used for both 800GbE and 1.6TbE) decreases and their efficiency improves, the market for these high-speed solutions will expand.
Challenges
While the 800GbE and 1.6TbE markets are poised for rapid growth, challenges exist:
-
High costs: The upfront cost of 800GbE and 1.6TbE solutions, including transceivers and networking equipment, remains a hurdle, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
-
Integration complexity: Transitioning to 800GbE or 1.6TbE often requires significant infrastructure upgrades, including fiber optics, network equipment, and software solutions.
-
Standardization and ecosystem development: Full ecosystem readiness, including optical interconnects, transceivers, and switching hardware, is critical for rapid adoption.
Market outlook
The global 800GbE and 1.6TbE markets are set to grow substantially as data-intensive applications continue to push network speeds to their limits. The adoption of 800GbE is expected to be widespread by the year 2025 with 1.6TbE following as the next step in Ethernet evolution, enabling the highest-capacity, low-latency networks for cloud providers, telecom operators, and data-intensive enterprises.
The 800GbE and 1.6TbE market outlook
As data centers continue to evolve and the demand for faster, more efficient network infrastructure grows, the Ethernet market is progressing toward ever-higher speeds, with 800GbE and 1.6TbE technologies playing key roles. The need for higher bandwidth to support next-generation applications such as 5G, AI/ML, cloud computing, and IoT is pushing Ethernet technology to its limits. The 800GbE market alone is expected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 7.5% between 2024 and 2030 as the demand for high-speed, high-capacity connections grow across large-scale data centers and telecom networks.
Beyond 800GbE, the 1.6TbE market is gaining attention, representing the next leap in Ethernet technology for the most demanding applications in high-performance computing, telecom backbones, and data-intensive workloads. 1.6TbE solutions, with their ability to support 1.6 Terabits per second of throughput, will drive innovation in network scalability, enabling data centers to handle petabytes of data across global infrastructures.
Key drivers of the 800GbE and 1.6TbE markets
-
Rising data demand: The continuous explosion in data generated by cloud services, 5G, AI, machine learning, and big data analytics is pushing the demand for higher network speeds.
-
5G and beyond: The global rollout of 5G networks and future plans for 6G create significant bandwidth demands, making the adoption of 800GbE and 1.6TbE essential for telecom networks.
-
AI/ML and high-performance computing (HPC): AI/ML models, especially in real-time data processing and training, require massive bandwidth, further driving the need for higher Ethernet speeds.
-
Data center and telecom network evolution: Hyper-scale data centers along with telecom backbones require faster and more efficient solutions to scale with increasing user demand and data traffic.
800GbE market segmentation
The 800GbE market is anticipated to grow in various segments, including: 25G, 50G, 100G, 200G, and 400G Transition to 800GbE.
-
As 400GbE adoption becomes more widespread, 800GbE will provide a vital step forward, supporting applications with higher capacity, including cloud, telecom, and large-scale enterprise networks.
Key applications of 800GbE
1.6TbE market and outlook
The 1.6TbE standard, while still in its early stages, is expected to see significant deployment in the 2027-2032 window. This higher-speed technology will support the largest-scale data centers, telecom backbones, and emerging applications such as AI-driven network optimization and cloud-scale data processing. 1.6TbE is expected to follow 800GbE, leveraging breakthroughs in optical interconnects, SerDes technology, and advanced modulation techniques to enable ultra-high-speed, low-latency connections.
-
1.6TbE will be primarily driven by the demand for massive data throughput in cloud data centers, 5G/6G, and telecom infrastructures.
-
It will likely feature advanced optical transceivers to handle the enormous bandwidth requirements and the transition from 800GbE will offer a cost-effective step for large-scale operators.
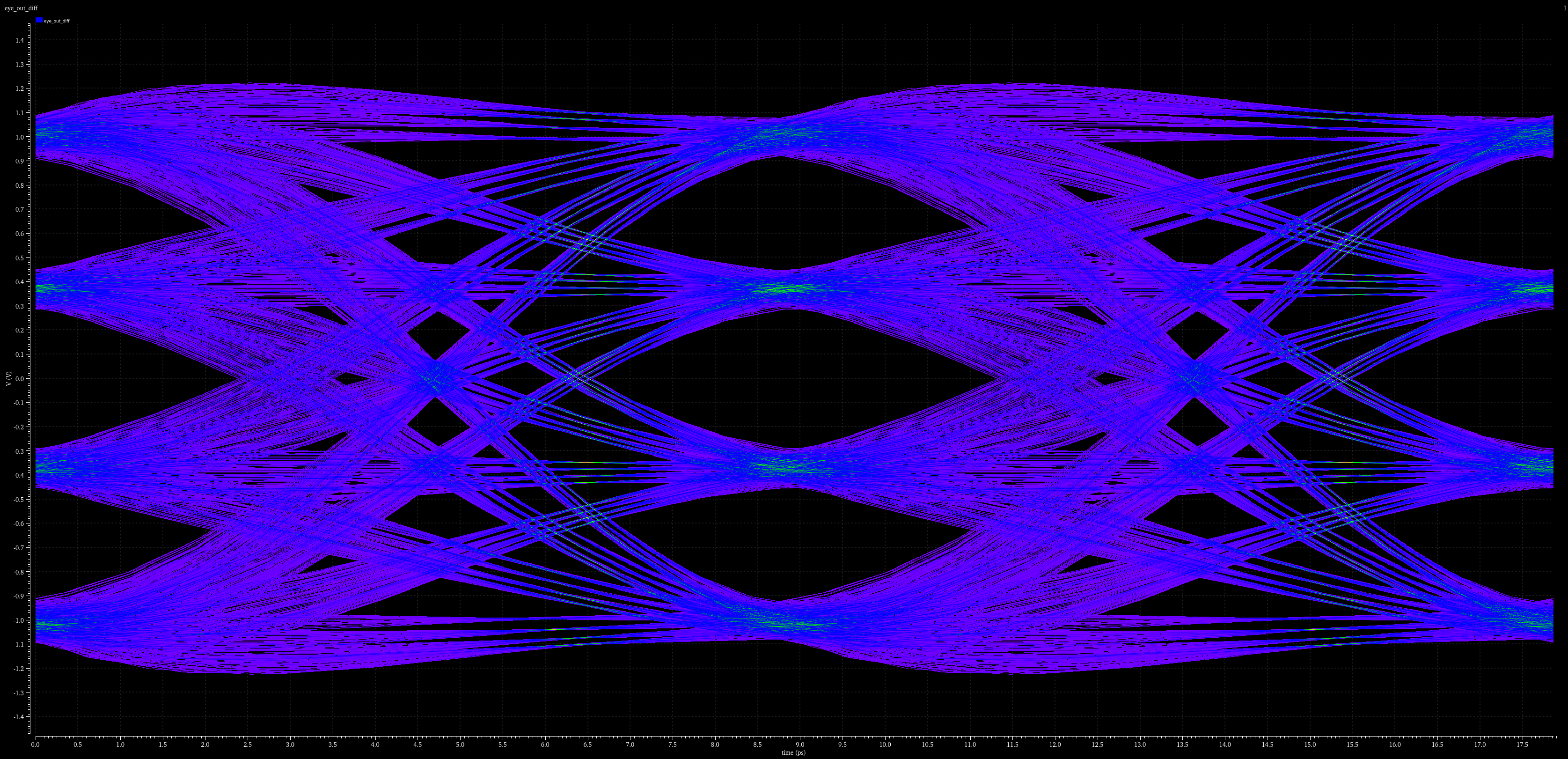
SerDes line rates and their impact on the 800GbE and 1.6TbE markets
The serial deserializer (SerDes) technology plays a pivotal role in enabling the high-speed transmission required for both 800GbE and 1.6TbE Ethernet technologies. SerDes operates by converting parallel data streams into serial data for high-speed transmission, and then converting it back for processing at the receiver end. Advances in SerDes technology will allow Ethernet speeds to scale beyond the current 400GbE limits, enabling 800GbE and 1.6TbE to become a reality.
SerDes line rates
-
SerDes for 800GbE: The typical line rate for 800GbE is 112 Gbps per lane, which uses PAM-4 (pulse amplitude modulation) for data transmission. The 400GbE standard uses 56 Gbps per lane, and 800GbE effectively doubles this, requiring optical interconnects capable of supporting higher speeds.
-
SerDes for 1.6TbE: The line rate for 1.6TbE is 224 Gbps per lane, also using PAM-4 modulation. This provides a significant boost in speed, enabling ultra-fast transmission for high-demand applications like large-scale cloud infrastructures, 5G backhaul, and high-performance computing (HPC).
Key drivers for growth
-
5G and beyond: The global deployment of 5G and future 6G networks will significantly push the need for higher-speed Ethernet solutions to meet the demands for ultra-low-latency and massive bandwidth.
-
Cloud computing: Cloud and hyperscale data centers are some of the largest consumers of bandwidth and will be key adopters of 800GbE and 1.6TbE technologies.
-
Telecom network upgrades: Telecom providers will be at the forefront of 1.6TbE adoption, as they need the next level of performance to support 5G backhaul and large-scale infrastructure.
-
Cost reduction in optical transceivers: As the cost of optical transceivers (used for both 800GbE and 1.6TbE) decreases and their efficiency improves, the market for these high-speed solutions will expand.
Challenges
While the 800GbE and 1.6TbE markets are poised for rapid growth, challenges exist:
-
High costs: The upfront cost of 800GbE and 1.6TbE solutions, including transceivers and networking equipment, remains a hurdle, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
-
Integration complexity: Transitioning to 800GbE or 1.6TbE often requires significant infrastructure upgrades, including fiber optics, network equipment, and software solutions.
-
Standardization and ecosystem development: Full ecosystem readiness, including optical interconnects, transceivers, and switching hardware, is critical for rapid adoption.
Market outlook
The global 800GbE and 1.6TbE markets are set to grow substantially as data-intensive applications continue to push network speeds to their limits. The adoption of 800GbE is expected to be widespread by the year 2025 with 1.6TbE following as the next step in Ethernet evolution, enabling the highest-capacity, low-latency networks for cloud providers, telecom operators, and data-intensive enterprises.

The 800GbE and 1.6TbE market outlook
As data centers continue to evolve and the demand for faster, more efficient network infrastructure grows, the Ethernet market is progressing toward ever-higher speeds, with 800GbE and 1.6TbE technologies playing key roles. The need for higher bandwidth to support next-generation applications such as 5G, AI/ML, cloud computing, and IoT is pushing Ethernet technology to its limits. The 800GbE market alone is expected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 7.5% between 2024 and 2030 as the demand for high-speed, high-capacity connections grow across large-scale data centers and telecom networks.
Beyond 800GbE, the 1.6TbE market is gaining attention, representing the next leap in Ethernet technology for the most demanding applications in high-performance computing, telecom backbones, and data-intensive workloads. 1.6TbE solutions, with their ability to support 1.6 Terabits per second of throughput, will drive innovation in network scalability, enabling data centers to handle petabytes of data across global infrastructures.

Key drivers of the 800GbE and 1.6TbE markets
-
Rising data demand: The continuous explosion in data generated by cloud services, 5G, AI, machine learning, and big data analytics is pushing the demand for higher network speeds.
-
5G and beyond: The global rollout of 5G networks and future plans for 6G create significant bandwidth demands, making the adoption of 800GbE and 1.6TbE essential for telecom networks.
-
AI/ML and high-performance computing (HPC): AI/ML models, especially in real-time data processing and training, require massive bandwidth, further driving the need for higher Ethernet speeds.
-
Data center and telecom network evolution: Hyper-scale data centers along with telecom backbones require faster and more efficient solutions to scale with increasing user demand and data traffic.
800GbE market segmentation
The 800GbE market is anticipated to grow in various segments, including: 25G, 50G, 100G, 200G, and 400G Transition to 800GbE.
-
As 400GbE adoption becomes more widespread, 800GbE will provide a vital step forward, supporting applications with higher capacity, including cloud, telecom, and large-scale enterprise networks.
Key applications of 800GbE

Telecom infrastructure will increasingly rely on 800GbE for high-speed connectivity, especially as 5G networks deploy
Telecom networks

800GbE supports faster processing of large datasets for AI model training and inference, essential in research and business applications
AI/ML

Scaling cloud services, especially in edge computing, requires networks that can handle high data throughput efficiently
Cloud data centers
1.6TbE market and outlook
The 1.6TbE standard, while still in its early stages, is expected to see significant deployment in the 2027-2032 window. This higher-speed technology will support the largest-scale data centers, telecom backbones, and emerging applications such as AI-driven network optimization and cloud-scale data processing. 1.6TbE is expected to follow 800GbE, leveraging breakthroughs in optical interconnects, SerDes technology, and advanced modulation techniques to enable ultra-high-speed, low-latency connections.
-
1.6TbE will be primarily driven by the demand for massive data throughput in cloud data centers, 5G/6G, and telecom infrastructures.
-
It will likely feature advanced optical transceivers to handle the enormous bandwidth requirements and the transition from 800GbE will offer a cost-effective step for large-scale operators.
SerDes line rates and their impact on the 800GbE and 1.6TbE markets
The serial deserializer (SerDes) technology plays a pivotal role in enabling the high-speed transmission required for both 800GbE and 1.6TbE Ethernet technologies. SerDes operates by converting parallel data streams into serial data for high-speed transmission, and then converting it back for processing at the receiver end. Advances in SerDes technology will allow Ethernet speeds to scale beyond the current 400GbE limits, enabling 800GbE and 1.6TbE to become a reality.
SerDes line rates
-
SerDes for 800GbE: The typical line rate for 800GbE is 112 Gbps per lane, which uses PAM-4 (pulse amplitude modulation) for data transmission. The 400GbE standard uses 56 Gbps per lane, and 800GbE effectively doubles this, requiring optical interconnects capable of supporting higher speeds.
-
SerDes for 1.6TbE: The line rate for 1.6TbE is 224 Gbps per lane, also using PAM-4 modulation. This provides a significant boost in speed, enabling ultra-fast transmission for high-demand applications like large-scale cloud infrastructures, 5G backhaul, and high-performance computing (HPC).
Key drivers for growth
-
5G and beyond: The global deployment of 5G and future 6G networks will significantly push the need for higher-speed Ethernet solutions to meet the demands for ultra-low-latency and massive bandwidth.
-
Cloud computing: Cloud and hyperscale data centers are some of the largest consumers of bandwidth and will be key adopters of 800GbE and 1.6TbE technologies.
-
Telecom network upgrades: Telecom providers will be at the forefront of 1.6TbE adoption, as they need the next level of performance to support 5G backhaul and large-scale infrastructure.
-
Cost reduction in optical transceivers: As the cost of optical transceivers (used for both 800GbE and 1.6TbE) decreases and their efficiency improves, the market for these high-speed solutions will expand.
Challenges
While the 800GbE and 1.6TbE markets are poised for rapid growth, challenges exist:
-
High costs: The upfront cost of 800GbE and 1.6TbE solutions, including transceivers and networking equipment, remains a hurdle, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
-
Integration complexity: Transitioning to 800GbE or 1.6TbE often requires significant infrastructure upgrades, including fiber optics, network equipment, and software solutions.
-
Standardization and ecosystem development: Full ecosystem readiness, including optical interconnects, transceivers, and switching hardware, is critical for rapid adoption.
Market outlook
The global 800GbE and 1.6TbE markets are set to grow substantially as data-intensive applications continue to push network speeds to their limits. The adoption of 800GbE is expected to be widespread by the year 2025 with 1.6TbE following as the next step in Ethernet evolution, enabling the highest-capacity, low-latency networks for cloud providers, telecom operators, and data-intensive enterprises.


